Omega-3 supplementation becomes appropriate when conventional dry eye treatments provide insufficient relief, symptoms persist despite artificial tear use, or underlying inflammatory processes require nutritional intervention. Strategic timing involves recognising specific symptom patterns, severity indicators, and treatment response limitations that omega 3 for eyes therapy could provide meaningful therapeutic benefits. Consider supplementation when experiencing meibomian gland dysfunction, chronic ocular surface inflammation, or environmental dry eye triggers that artificial tears cannot adequately address through surface lubrication alone.
Persistent symptom recognition
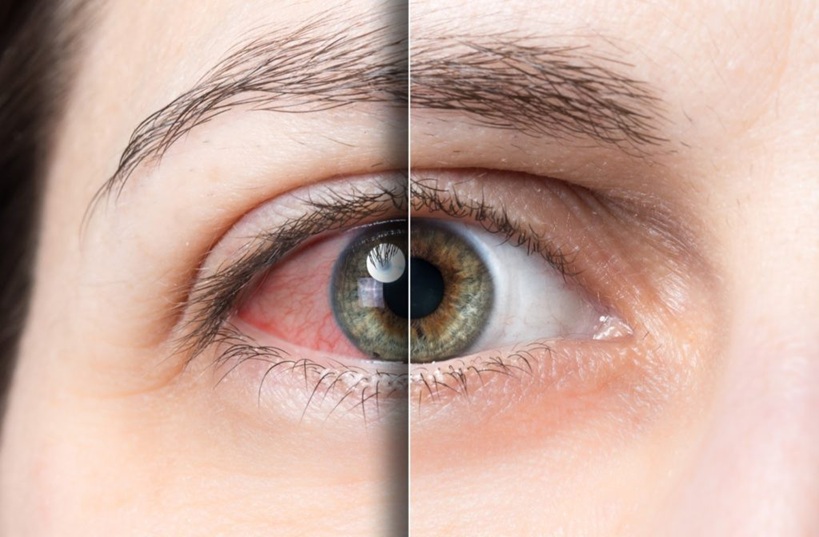
Consider omega-3 intervention when dry eye symptoms persist beyond three months despite consistent artificial tear use, indicating that surface lubrication alone cannot address underlying biochemical deficiencies affecting tear film stability. Persistent symptoms include burning sensations, gritty feelings, fluctuating vision, and eye fatigue that interfere with daily activities. Chronic symptom patterns often indicate inflammatory processes or meibomian gland dysfunction that require systemic nutritional support rather than topical treatments alone. Omega-3 fatty acids address these underlying causes through anti-inflammatory mechanisms and improved lipid layer production that artificial tears cannot replicate.
Artificial tear limitations
Omega-3 supplementation becomes valuable when artificial tears provide only temporary relief, requiring frequent daily reapplication. This suggests that tear film instability stems from compositional deficiencies rather than simple volume inadequacy that topical lubricants can address effectively. Limitation indicators include the need for artificial tear use every 1-2 hours, poor symptom relief duration, inadequate comfort improvement, and continued symptoms despite maximum artificial tear frequency. These patterns suggest underlying tear film dysfunction requiring systemic intervention through nutritional support.
Meibomian gland dysfunction
Consider omega-3 therapy when experiencing thick, cloudy meibomian gland secretions, lid margin inflammation, or blocked oil glands that artificial tears cannot address. These conditions require improved lipid layer composition rather than additional surface lubrication.
- Thick, paste-like meibomian secretions indicate poor oil gland function and lipid quality
- Inflamed eyelid margins with crusting, scaling, or redness affecting meibomian gland openings
- Blocked oil glands prevent normal lipid layer formation and tear film stabilisation
- Poor tear film breakup time indicates inadequate lipid layer protection against evaporation
- Recurrent chalazion or stye formation suggests chronic meibomian gland inflammation and dysfunction
Meibomian dysfunction requires systemic anti-inflammatory support and improved lipid metabolism, which omega-3 fatty acids can provide through enhanced gland function and reduced inflammatory processes affecting oil production.
Treatment timeline expectations
Omega-3 therapy consideration should occur early in dry eye management rather than as a last resort, since fatty acid tissue incorporation requires 6-12 weeks for meaningful therapeutic effects. At the same time, conventional treatments provide only symptomatic relief without addressing underlying causes.
- Early intervention timing maximises therapeutic potential before chronic inflammatory changes develop
- Realistic expectation setting regarding a 6-12 week timeframe for noticeable symptom improvement
- Combination therapy approach using omega-3 alongside conventional treatments for optimal outcomes
- Progressive symptom monitoring, evaluating improvement patterns, and treatment response
- Long-term commitment recognition since omega-3 benefits require sustained supplementation for maintenance
Timeline considerations emphasise patience and consistency while recognising that omega-3 therapy addresses root causes rather than providing immediate symptomatic relief like artificial tears. Optimal timing involves early consideration rather than last-resort thinking, allowing adequate time for fatty acid tissue incorporation and anti-inflammatory effects to develop. Success requires realistic expectations about therapeutic timelines while maintaining consistent supplementation alongside conventional treatments for comprehensive dry eye management that addresses both symptoms and underlying causes.